Health Packages

CBC Test
A Complete Blood Count (CBC) test is a common blood test used to assess overall health and detect a wide range of disorders, such as anemia, infection, and leukemia. It measures various components of the blood, including red blood cells, white blood cells, hemoglobin, hematocrit, and platelets. The test provides valuable information about the body’s ability to fight infection, carry oxygen, and clot blood, and helps monitor chronic conditions.
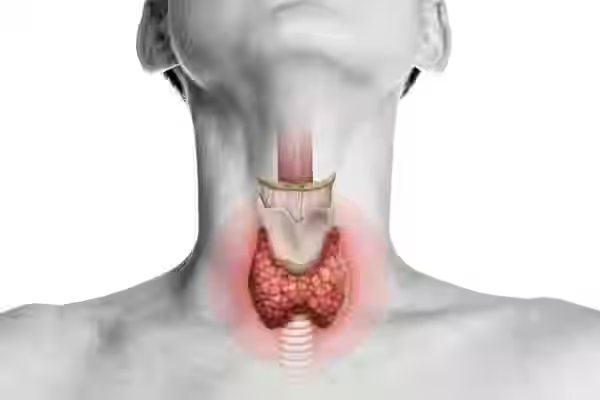
Thyroid Profile Test
A thyroid profile test measures the levels of thyroid hormones in the blood, including Thyroxine (T4), Triiodothyronine (T3), and Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH). These hormones regulate metabolism, energy production, and overall body functions. The test is used to diagnose thyroid disorders such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism. Accurate detection through this test allows for early intervention and effective management of thyroid conditions.

C Reactive Protein Test
The C-reactive protein (CRP) test measures the level of CRP in the blood, which rises in response to inflammation. This test is commonly used to detect acute infections, autoimmune disorders, or chronic inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Elevated CRP levels may also indicate a higher risk of cardiovascular disease, as inflammation plays a role in the development of atherosclerosis.
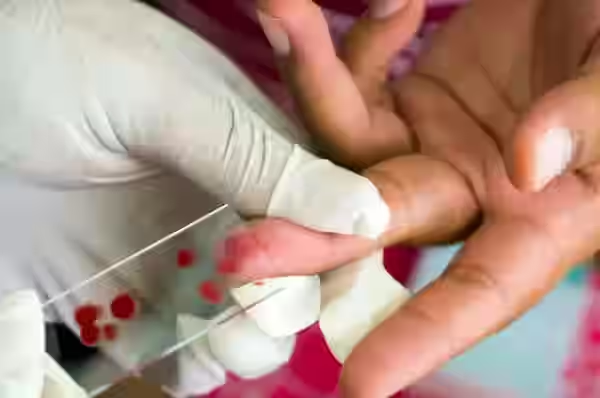
Malaria Test
The malaria test is a diagnostic procedure used to detect the presence of Plasmodium parasites, which cause malaria, in the blood. There are various types of malaria tests, including rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs) and microscopy, both of which identify the parasite in blood samples. This test is crucial for diagnosing malaria in patients who present with symptoms like fever, chills, and flu-like symptoms, especially if they have recently traveled to malaria-endemic areas. Early detection through this test allows for prompt treatment with antimalarial medications, reducing the risk of severe complications such as organ failure, anemia, or death.
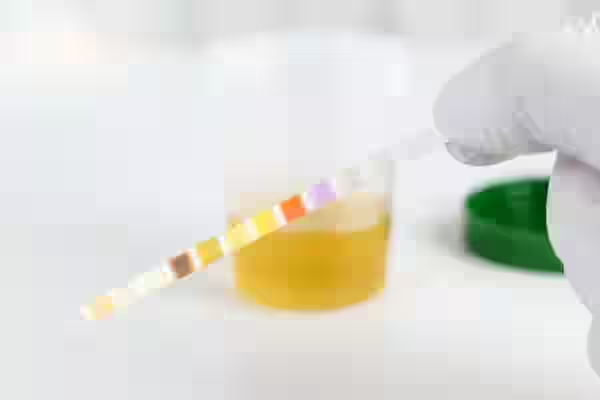
Urine Culture Test
A urine culture test is a diagnostic procedure used to detect the presence of bacteria, fungi, or other microorganisms in the urine, which may indicate a urinary tract infection (UTI). The urine sample is cultured in a laboratory, allowing the organisms to grow over a period of time, typically 24 to 48 hours. Once identified, sensitivity testing is done to determine which antibiotics will be most effective for treatment. This test is essential in cases of recurrent UTIs, unexplained urinary symptoms, or when previous treatments have failed. Early detection and targeted treatment through urine culture can prevent complications and ensure a faster recovery.
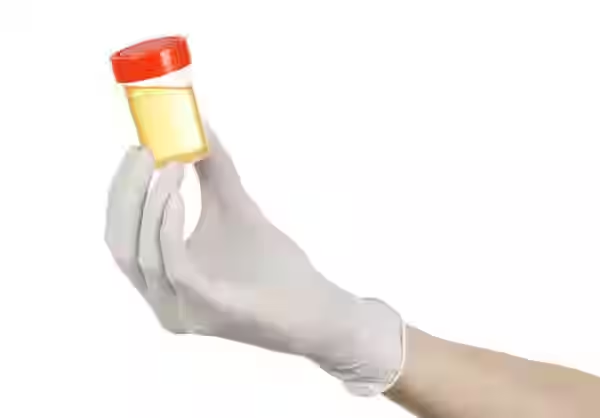
Urine Analysis Test
A urine analysis test is a diagnostic tool used to evaluate the composition of a urine sample, assessing its physical, chemical, and microscopic properties. This test helps in diagnosing a wide range of medical conditions, including kidney disorders, urinary tract infections, diabetes, and liver diseases. Components like color, clarity, pH, specific gravity, glucose, proteins, and the presence of cells or microorganisms are analyzed to provide insights into the patients overall health. A urine analysis test is often part of routine health checkups and is essential for early detection of diseases, guiding treatment decisions and monitoring ongoing health conditions.

Urine Routine Test
A urine routine test is a comprehensive examination of a urine sample that checks for various parameters such as pH, glucose, proteins, ketones, red blood cells, white blood cells, and the presence of bacteria or other substances. This test provides valuable information about kidney function, urinary tract infections (UTIs), metabolic conditions like diabetes, and other health concerns. The test is simple, non-invasive, and widely used in routine health check-ups and diagnostic screenings. Results from a urine routine test can help detect infections, inflammation, or abnormalities in the urinary system, enabling early intervention and treatment.

Urine Test For Pregnancy
A urine test for pregnancy is a quick and reliable method to confirm pregnancy by detecting the presence of the hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in a woman’s urine. This hormone is produced by the placenta shortly after a fertilized egg attaches to the uterine lining. The test is commonly performed at home using over-the-counter kits, though it can also be done in a clinical setting for more accurate results. The test is typically accurate after a missed period, with most kits providing results within minutes. Confirming pregnancy early allows women to start appropriate prenatal care and make necessary lifestyle adjustments.

Urine Sugar & Protein Test
The urine sugar and proteins test is a diagnostic procedure used to detect the presence of glucose (sugar) and proteins in urine. Normally, urine should not contain significant amounts of either substance, and their presence may indicate underlying health issues. Elevated glucose levels in urine are often associated with diabetes, while protein in urine (proteinuria) can be a sign of kidney disease, high blood pressure, or other medical conditions. This test is simple and non-invasive, involving the collection of a urine sample for laboratory analysis. Early detection through this test can help diagnose and manage conditions that affect the kidneys, pancrea.

Stool Analysis Test
A stool analysis is a laboratory test used to examine a sample of stool (feces) to diagnose various gastrointestinal conditions. The test can detect blood, bacteria, parasites, fat content, and the presence of abnormal cells or substances that may indicate digestive disorders, infections, or diseases like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) or colon cancer. The physical characteristics of the stool, such as color, consistency, and odor, are also analyzed. This test is essential for identifying causes of symptoms like diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, or weight loss. Early detection of issues through stool analysis can lead to more effective treatment and improved outcomes.

Stool Culture Test
A stool culture test is a diagnostic procedure used to detect harmful bacteria, viruses, or parasites in a stool sample that may be causing gastrointestinal symptoms such as diarrhea, vomiting, or abdominal pain. The stool sample is cultured in a lab to encourage the growth of microorganisms, which are then identified and tested for sensitivity to antibiotics. This test is essential for diagnosing infections like salmonella, E. coli, or Clostridium difficile. Prompt diagnosis through a stool culture allows for targeted treatment, helping to resolve symptoms quickly and prevent the spread of infection, especially in cases of foodborne illness or outbreaks.

Stool Test Hanging Drop
The stool hanging drop test is a specific diagnostic procedure used to identify motile organisms, such as the Vibrio cholerae bacteria, which causes cholera. In this test, a small drop of stool is placed on a glass slide, and the movement of the bacteria is observed under a microscope. This method helps in the rapid detection of cholera and other bacterial infections that involve motile organisms. The test is typically performed in areas where cholera outbreaks are common, or when patients present with symptoms like severe diarrhea. Early diagnosis through this test enables prompt treatment, reducing the risk of complications and preventing the spread of infection.

Stool pH Test
The stool pH test measures the acidity or alkalinity of a stool sample, which can provide valuable insights into digestive health. Abnormal stool pH levels may indicate conditions such as lactose intolerance, bacterial infections, or malabsorption syndromes. For instance, an acidic stool pH may suggest carbohydrate malabsorption, while an alkaline stool pH could indicate a disruption in the normal bacterial flora of the intestines. This simple, non-invasive test is often used in conjunction with other diagnostic tests to identify gastrointestinal disorders and guide appropriate treatment. Monitoring stool pH can help manage digestive health and prevent complications.

Prothrombin Time Test
The prothrombin time (PT) test is a blood test used to measure how long it takes for blood to clot. This test evaluates the function of specific clotting factors and is commonly used to monitor patients taking blood-thinning medications like warfarin or to diagnose bleeding disorders. Prolonged clotting times may indicate conditions such as liver disease, vitamin K deficiency, or a clotting factor deficiency. The PT test is essential for ensuring that patients on anticoagulant therapy are receiving the correct dosage to prevent excessive bleeding or the formation of dangerous blood clots. Regular monitoring through this test helps maintain the balance of blood clotting in body.
Glucose Plasma Test
The glucose plasma test is a blood test that measures the concentration of glucose (sugar) in the blood plasma. It is commonly used to diagnose and monitor conditions such as diabetes and prediabetes. This test can be done in a fasting state (fasting blood glucose test) or at any time (random glucose test). High levels of glucose in the blood may indicate that the body is not using insulin properly, which is a key feature of diabetes. Monitoring blood glucose levels is crucial for managing diabetes and preventing complications such as cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, or neuropathy. The glucose plasma test is a vital tool for maintaining overall health.
Plasma Fibrinogen Test
The plasma fibrinogen test measures the amount of fibrinogen, a protein in the blood that plays a key role in blood clotting. Low levels of fibrinogen can lead to excessive bleeding, while high levels may indicate an increased risk of blood clots, which can lead to conditions like deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or heart attacks. This test is often used to assess bleeding disorders, monitor patients undergoing anticoagulant therapy, or evaluate the risk of cardiovascular disease. It is also used in the diagnosis of conditions like disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) or liver disease, where fibrinogen levels can be affected.
Ammonia Test
The ammonia (EDTA/plasma) test measures the level of ammonia in the blood, which can indicate liver dysfunction or certain metabolic conditions. Ammonia is a waste product produced by the body during the digestion of proteins, and the liver normally converts it into urea for excretion. Elevated levels of ammonia in the blood may suggest liver disease, such as cirrhosis or hepatitis, or a condition like Reye’s syndrome, which affects the brain and liver. This test is essential for diagnosing and monitoring patients with liver disease, encephalopathy, or other conditions that affect the body’s ability to process.
Toxoplasma (IgM) Test
The Toxoplasma IgM test is a blood test used to detect the presence of IgM antibodies, which are produced by the immune system in response to an infection with the Toxoplasma gondii parasite. This test is particularly important for pregnant women, as an infection with Toxoplasma during pregnancy can lead to congenital toxoplasmosis, a serious condition that can cause birth defects. The IgM test helps identify acute infections, distinguishing them from past infections where IgG antibodies are present. Early detection through this test allows for prompt treatment to reduce the risk of complications for both mother & baby.
SARS CoV-2 (COVID) RT PCR Test
The SARS CoV-2 (COVID-19) RT-PCR test is a molecular diagnostic test used to detect the presence of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, responsible for the COVID-19 disease. It works by amplifying viral RNA from a sample taken via nasal or throat swabs, providing a highly accurate result even in early stages of infection. This test is considered the gold standard for diagnosing COVID-19 due to its high sensitivity and specificity. RT-PCR is widely used for screening symptomatic individuals, contacts of confirmed cases, and travelers. A positive test confirms infection, enabling timely isolation and treatment, while a negative result rules out active infection.

Nasal Swab Culture & Sensitivity Test
A nasal swab culture and sensitivity test is a diagnostic procedure used to identify infections in the nasal cavity. A sample is collected from the nasal passages using a sterile swab, and this sample is cultured in a laboratory to grow any bacteria or viruses that may be present. The sensitivity part of the test helps determine which antibiotics or antiviral medications will be most effective in treating the infection. This test is commonly used to diagnose respiratory infections like the flu, sinusitis, or bacterial infections such as MRSA. Early detection through this test enables timely and targeted treatment, improving recovery outcomes.
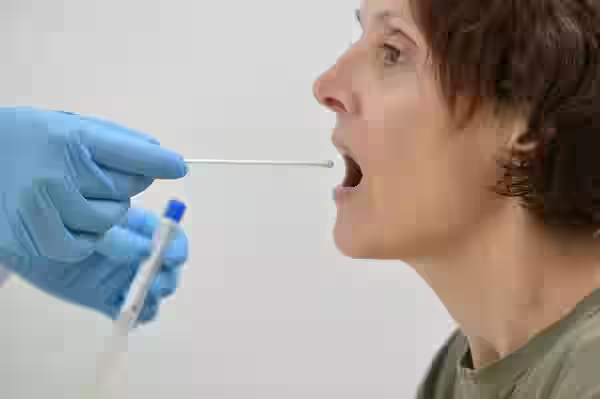
Throat Swab Culture & Sensitivity Test
The throat swab culture and sensitivity test is a diagnostic tool used to detect bacterial or viral infections in the throat, particularly those causing sore throat or pharyngitis. The test involves taking a swab from the back of the throat and tonsils, which is then cultured in a lab to identify the causative organism. Once the infection is identified, a sensitivity test determines the most effective antibiotics or antiviral medications for treatment. This test is particularly useful in diagnosing bacterial infections like Streptococcus (strep throat) and can prevent complications by guiding appropriate treatment. It is quick, non-invasive, and widely used in clinical settings.

